Hosting
Questions
Answers
What is hosting?
Hosting is a service that allows individuals and organizations to place their websites or web applications on the internet. Essentially, a hosting provider offers space on its server and ensures a constant internet connection so that your site is accessible to users around the clock.
Main Aspects of Hosting
Server Space: You are allocated a certain amount of disk space on the server to store your site's files—HTML, CSS, images, videos, and other resources.
Internet Connection: Servers are constantly connected to high-speed internet networks, ensuring fast loading times for your site and accessibility for users at any time and from anywhere in the world.
Technical Support: Round-the-clock technical support is provided to help resolve issues related to your site's operation, server setup, and other technical aspects.
Security: Basic protection from cyberattacks is ensured, SSL certificates are offered for data encryption, and additional services for data backup are provided.
Types of Hosting
1. Shared Hosting:
Description: Multiple sites are hosted on a single physical server and share its resources (processor, RAM, disk space).
Advantages: Cost-effective and easy to manage.
Disadvantages: Limited resources and dependence on the load from other sites on the server.
2. Virtual Private Server (VPS):
Description: The server is divided into virtual servers, each functioning as a separate dedicated server with guaranteed resources.
Advantages: More control, stability, and scalability.
Disadvantages: Requires some technical skills and is more expensive than shared hosting.
3. Dedicated Server:
Description: An entire physical server is provided for the use of one client.
Advantages: Maximum performance and full control over the server.
Disadvantages: Requires administrative experience and is more expensive than a virtual server.
Description: Your site uses the resources of multiple servers combined into a "cloud."
Advantages: High reliability, flexibility in resource usage, and scalability.
Why Do You Need Hosting?
Availability: Hosting ensures constant access to your site for all users, regardless of their location and time of day.
Data Storage: Provides a secure place to store all files, databases, and other information necessary for your site's operation.
Performance: Quality hosting improves page load speed and the overall user experience of your site.
Security: Smart Ape offers various levels of protection against malicious attacks, viruses, and data loss.
Scalability: Allows you to easily increase resources (disk space, RAM, processor power) as your site grows and traffic increases.
Advantages of Smart Ape:
Reliability and Uptime: We guarantee the availability of our resources 99.982% of the time.
Speed and Performance: Our servers ensure fast loading times for your site.
Unlimited Internet: A 1 Gbps channel for each dedicated server. Average monthly traffic up to 100 Mbps is free; 200 Mbps for a virtual server; 100 Mbps for shared hosting.
Technical Support: Round-the-clock and competent support for quick resolution of potential issues.
Security: All servers are connected to basic DDoS attack protection. Additional continuous protection can be enabled.
Conclusion
Hosting is a fundamental component of your online presence. Without hosting, your site cannot be accessible to users. Choosing the right type of hosting significantly affects the success of your web project, including its performance, security, and ability to scale with your needs.
How to choose a data center?
You can select a data center during the order process on the website, in the first tab "Settings" of the order configuration (see Fig.1).
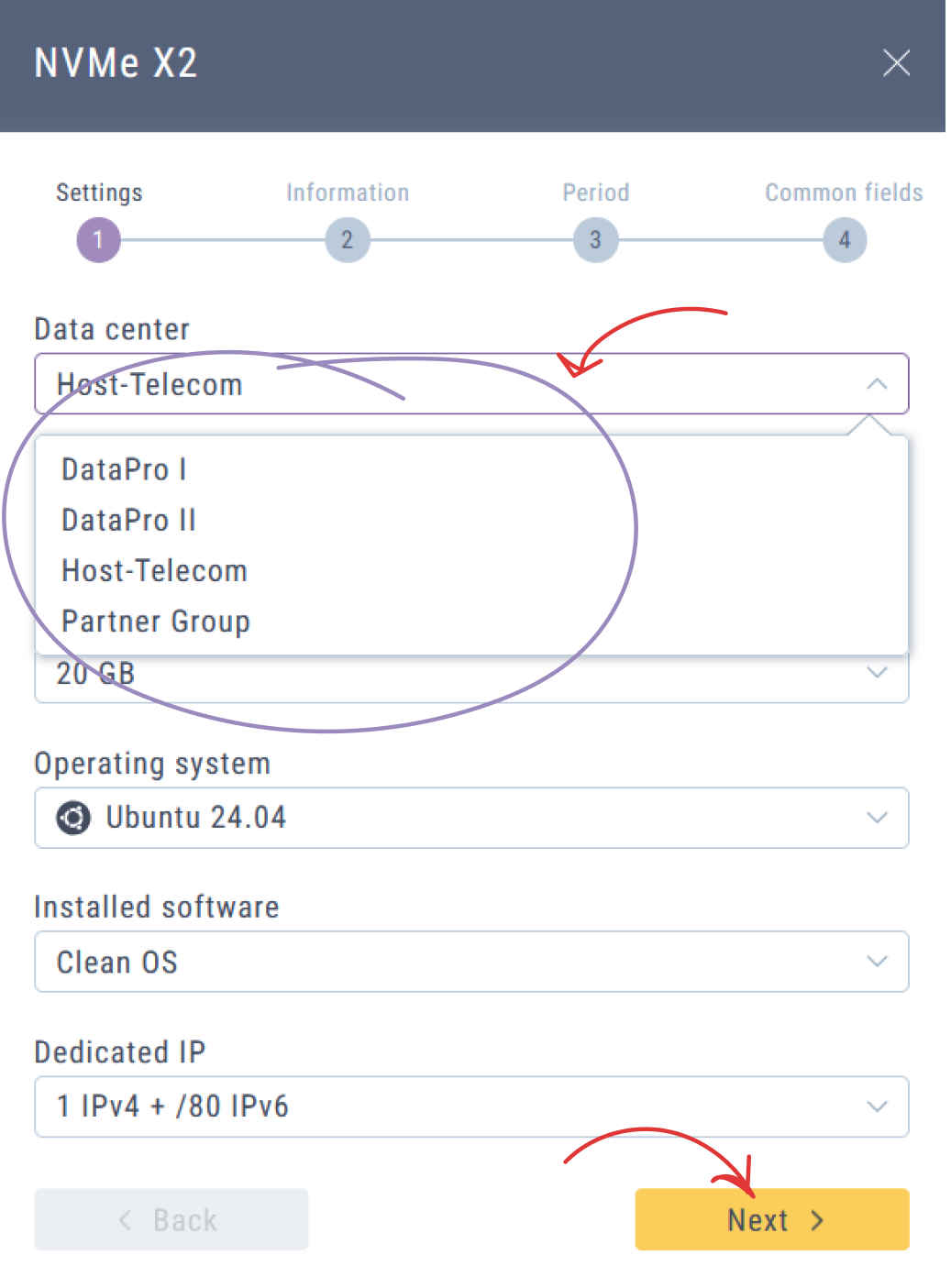
Fig.1
To select a data center for your service/server in the personal account, expand the corresponding menu on the service plan selection page (see Fig.2).
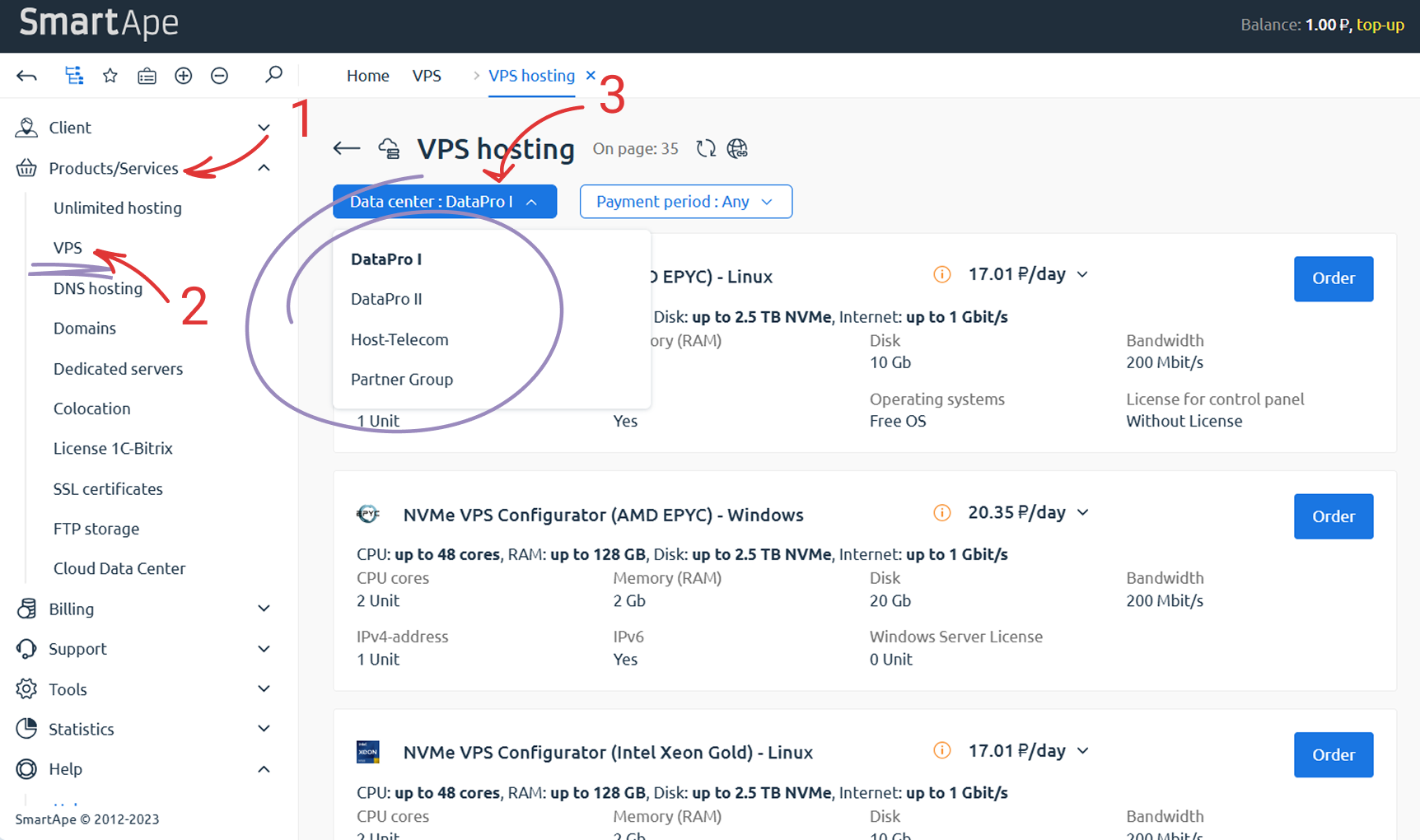
Fig.2
List of Available Data Centers:
Russia: DataPro Moscow I (RU), DataPro Moscow II (RU), DataPro Moscow III (RU)
Israel: Partner Group (IL)
Czech Republic: Host-Telecom (CZ)
For more information about data centers, visit the Data Centers page.
How to change the service configuration?
Modifying the Configuration (Resources) for Unlimited Hosting, Bitrix Hosting, VPS, Dedicated Server, and Cloud Data Center Services
To modify the configuration of your service, follow these steps:
- Log in to your account.
- Navigate to the "Products/Services" section.
- Select the required service.
- Highlight the row with the desired service number and click "Edit" (see Fig.1).
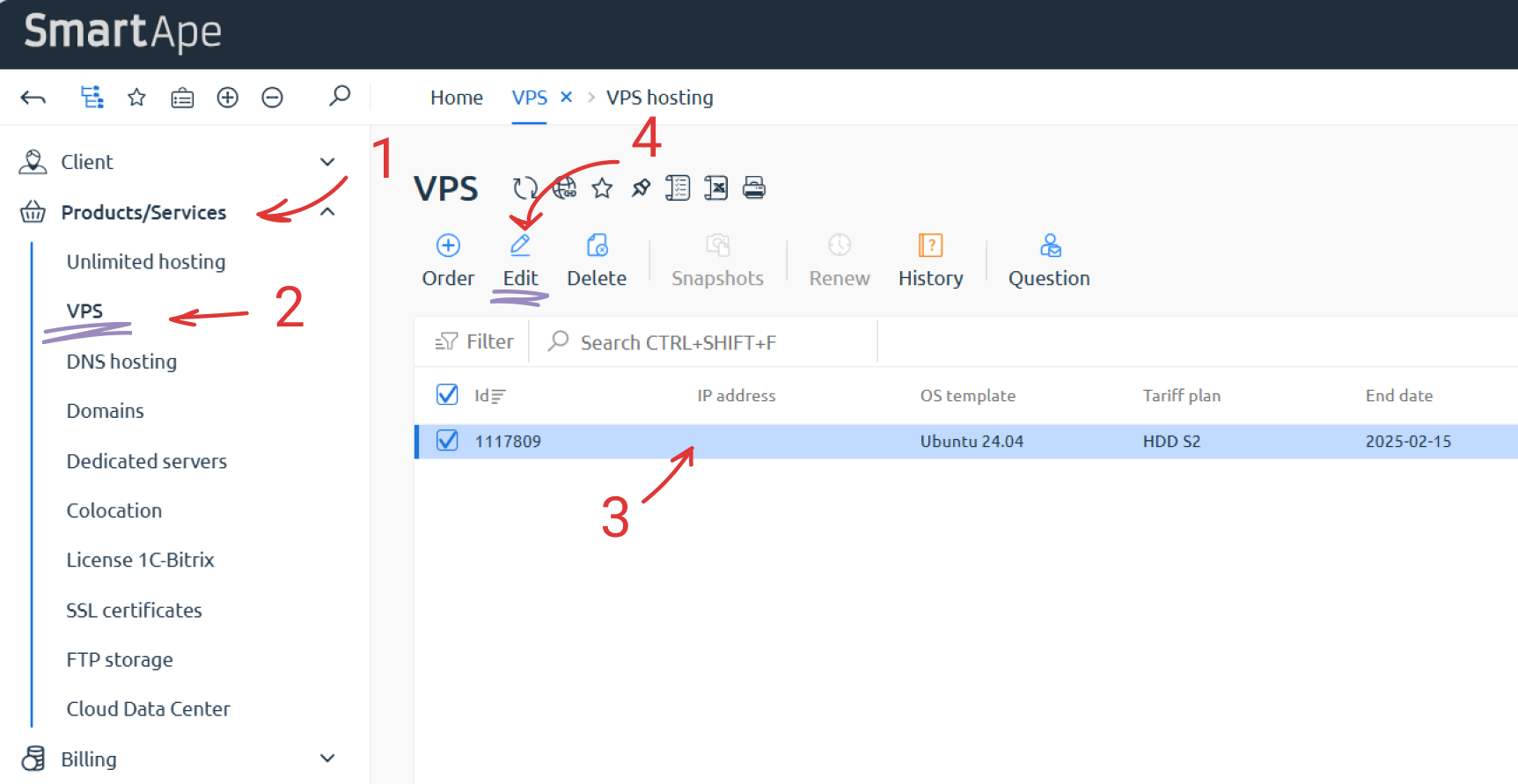
Fig.1
Example: Modifying VPS Configuration
In the "Products/Services" section, select "VPS".
Find the required service, highlight it, and click "Edit".
After making changes, the cost of the configuration modifications will be displayed at the bottom of the page.
To apply the changes, click "To shopping cart" (see Fig.2), then proceed to the cart and complete the payment using any available method.
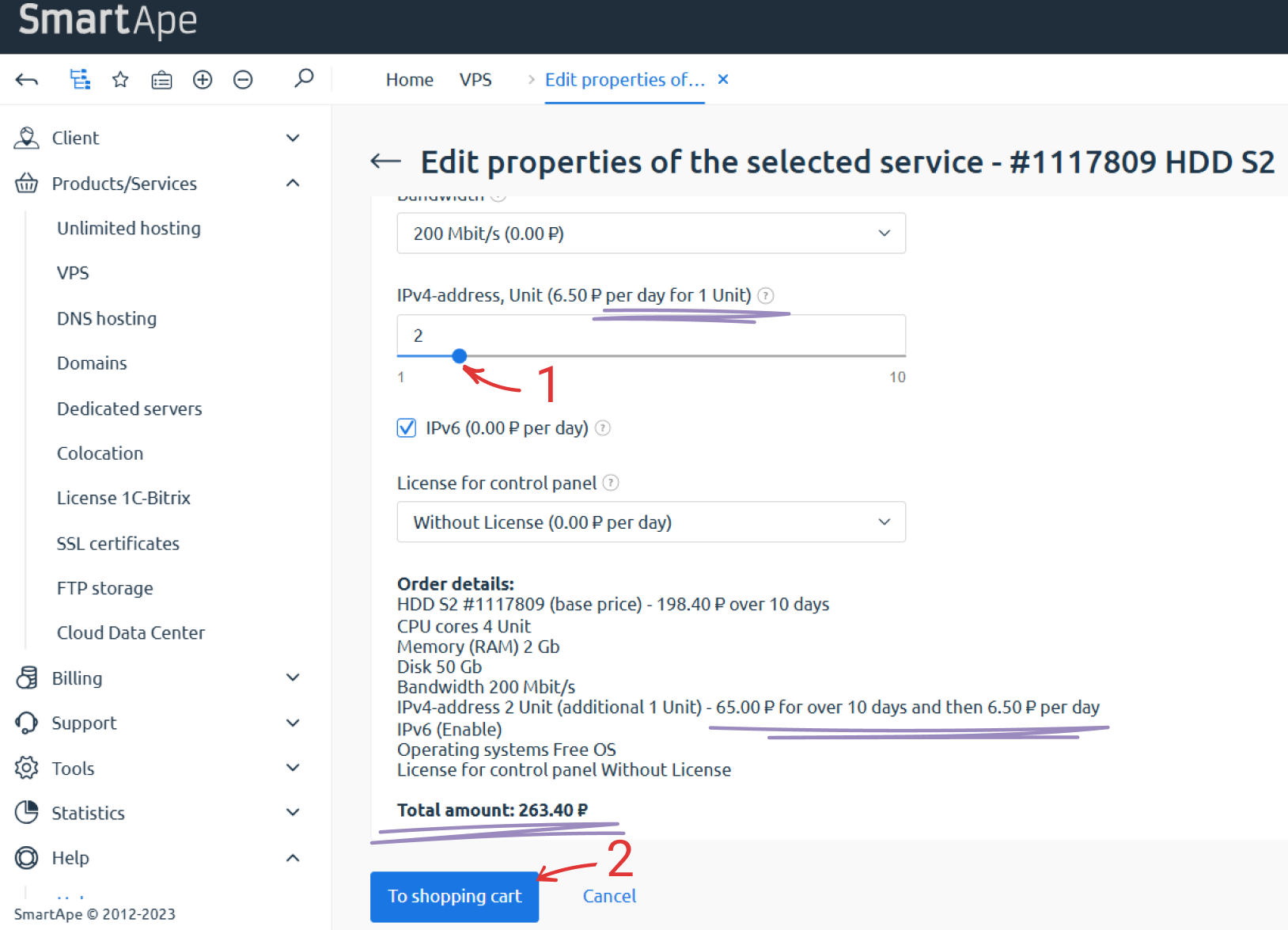
Fig.2
Features of Fixed VPS Tariffs
For plans such as HDD S1, HDD S2... NVMe X1, NVMe X2... Turbo R1, Turbo R2..., only disk space expansion is available.
- To increase RAM, CPU cores, or network bandwidth, you must upgrade to a higher-tier plan.
- When upgrading, all data on the server remains unchanged.
- Plan upgrades are available upon request to the Financial Department.
Flexible Resource Configuration
If you require frequent resource adjustments (RAM, CPU cores, network bandwidth), we recommend selecting a "Configurator" plan (indicated in the plan name). These configurable plans are available exclusively through the personal account.
Modifying a Dedicated Server Configuration
The process is similar to modifying a VPS configuration:
- Go to "Products/Services" → "Dedicated servers".
- Select the required server and make the necessary changes, following the VPS modification example.
- After payment, submit a request to the Technical Department, specifying:
Once the request is processed, the changes will be applied at the scheduled time.
Types of disks, which one to choose?
Choosing a Storage Drive for VPS and Dedicated Servers
Selecting the right storage drive is a key factor when configuring a VPS (Virtual Private Server) or a dedicated server. It affects performance, data access latency, database efficiency, and overall system stability.
Below is a breakdown of the available storage options, along with their benefits:
- SATA (HDD) – Traditional Hard Disk Drives
- SSD – Solid State Drives
- NVMe (SSD) – Next-generation SSDs using PCIe interface
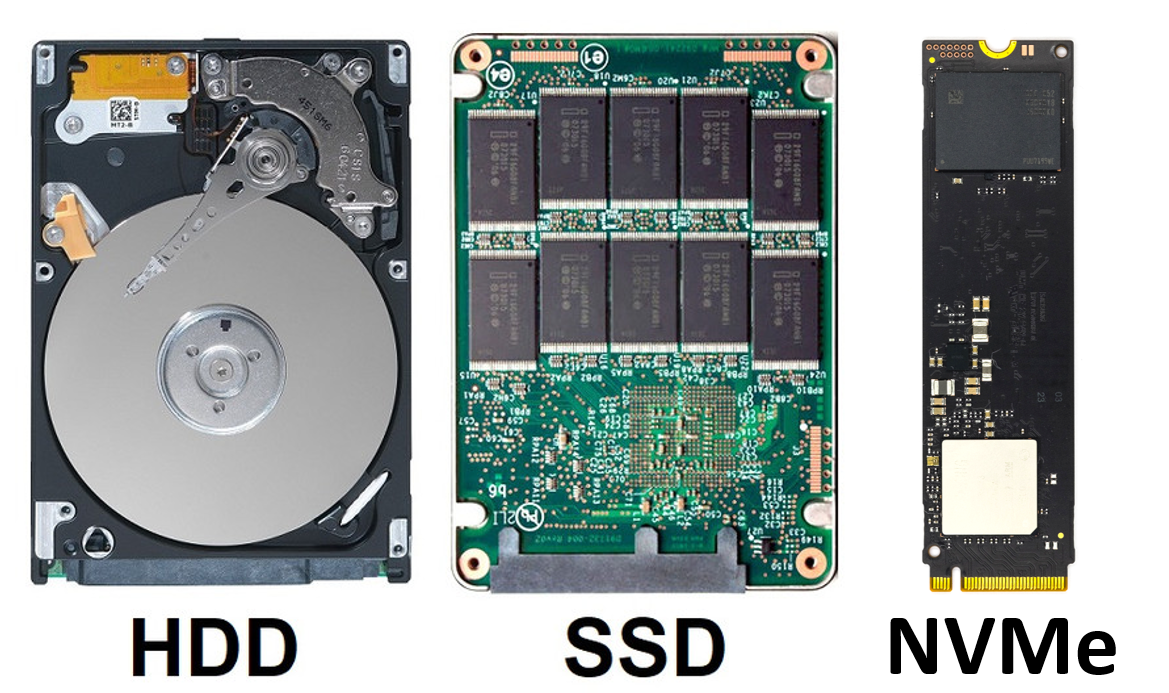
Type of disks
Let’s examine their features, advantages, and how they impact server performance.
1. SATA HDD (Hard Disk Drives with SATA Interface)
HDDs (Hard Disk Drives) use magnetic platters and a mechanical read/write head. They connect via the SATA (Serial ATA) interface, offering data transfer speeds of up to 6 Gbps (~600 MB/s), though real-world performance is lower due to mechanical limitations.
✅ Advantages of SATA HDD for Servers:
- High storage capacity – available up to 16TB.
- Low cost – cheaper than SSD and NVMe.
- Suitable for storing large volumes of data (archives, backups, media files).
❌ Disadvantages:
- Slow read/write speeds (100–200 MB/s).
- High latency due to mechanical operation.
- Mechanical components degrade over time.
📌 Best Use Cases:
- File storage, backup solutions, rarely accessed data.
- Not recommended for performance-intensive applications (databases, high-traffic web applications).
2. SSD (Solid State Drives with SATA or SAS Interface)
SSDs (Solid State Drives) use NAND flash memory instead of mechanical parts. They connect via the same SATA (or SAS for enterprise use) interface but offer significantly higher speeds than HDDs.
✅ Advantages of SSD for Servers:
- High read/write speeds – up to 550 MB/s (limited by SATA interface).
- Lower latency – 10–100x faster response time than HDDs.
- Greater reliability – no mechanical parts, resistant to vibrations.
❌ Disadvantages:
- Higher cost than HDDs (though prices are decreasing over time).
📌 Best Use Cases:
- Web servers, databases, virtualization, cloud solutions.
- Ideal for VPS environments where speed is crucial.
- Improves performance by reducing data access times.
3. NVMe SSD (Next-Generation Storage with PCIe Interface)
NVMe (Non-Volatile Memory Express) utilizes the PCIe interface instead of SATA, delivering speeds 5–7 times faster than standard SATA SSDs.
✅ Advantages of NVMe SSD for Servers:
- Maximum speed – read/write speeds up to 7000 MB/s (10x faster than SATA SSDs).
- Minimal latency – near-instant data access.
- Multithreading support – crucial for high-load servers.
- High reliability and long lifespan.
❌ Disadvantages:
- More expensive than HDDs (but costs are gradually decreasing).
- Requires compatible hardware (PCIe slots on motherboards).
📌 Best Use Cases:
- High-performance databases, financial transactions, Big Data.
- Servers handling intensive disk operations.
- VPS and dedicated servers requiring top-tier performance.
Which Storage Drive Should You Choose for VPS or Dedicated Servers?
- Budget-friendly option (archives, backups, basic websites) → SATA HDD
- Balance of speed and cost (websites, databases, virtual servers) → SATA SSD
- Maximum performance (high-traffic servers, critical data storage) → NVMe SSD
If your server processes databases, handles a high number of requests, or stores critical data, NVMe SSD is the best choice. For simple backup storage, SATA HDD is a cost-effective option.
Choose your storage drive based on your workload, budget, and server demands!
How to transfer hosting to your service?
1. To get started, register if you are not yet our client.
2. Follow the instruction "Transfer hosting to maintenance".
- In your personal account, click on the Order Service link.
- In the window that appears, replace the Product Type with "Domain name", click Next.
- Put a marker next to the Transfer domain name item, click Next.
- In the window that appears, enter the domain name.
- Select the domain zone, click Next.
- A window will appear to confirm the selection and set the payment amount. Click Next.
- If you selected Company in the contact type, then enter the company name. And if you have chosen a private person, then the full name of the person on whom the site is registered. Click Next.
- In the window that appears, enter information about the contact person. After entering, click Next.
- Entering contact information continues in the next window. Specify the ways in which you can contact the contact person.
- In the next window, enter your passport details, date of birth and TIN.
- The last step of entering contact information is entering the address.
- Click Next.
- Enter the last name and initials of the mail recipient, click Next and the request will be sent for processing.

